White Paper Maps out China's IPR Progress
Editor's note: Last year was of great significance for the IPR system in China. In addition to marking the 30th anniversary of the launch of reform and opening, it was also the inaugural year in the implementation of the national intellectual property (IP) strategy. The Chinese IPR system saw 828,328 patent applications and 698,000 applications for trademark registration last year.
After China launched its Compendium of the National Intellectual Property Strategy, the State Intellectual Property Office (SIPO) released the White Paper on China's intellectual property protection in 2008.
The White Paper is a summation of last year's IPR protection in China and includes eight parts detailing various aspects of intellectual property, including revision and amendment of legislation, enforcement of IPR, judicial protection, Olympic IPR protection and international IPR cooperation.
China Business Weekly will publish the full text of the White Paper in a series in the coming weeks. The first part about legislative advances in the field of IPR was published on May 4. Below is the second part of the text:
II. IPR examination and registration advance steadily with various missions accomplished
In 2008, both filings and grants increased rapidly. IPR examination and registration advanced steadily.
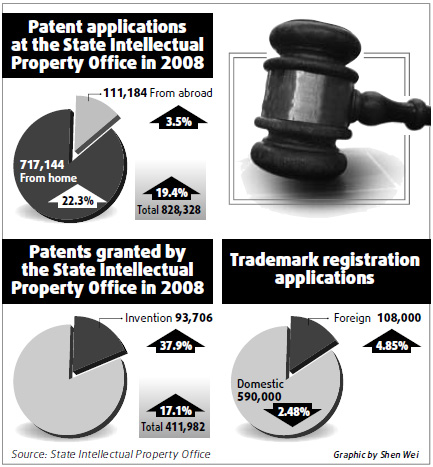
In 2008, patent applications maintained steady and relatively fast growth. SIPO received 828,328 patent applications, up 19.4 percent year-on-year; 717,144 of which were domestic, representing 86.6 percent of the total and up 22.3 percent; and 111,184 of which were from overseas, accounting for 13.4 percent of the total and up 3.5 percent.
As of Dec 31, 2008, China received accumulative 4.85 million patent applications, 4.03 million of which were domestic, representing 83 percent; and 825,113 of which were from overseas, accounting for 17 percent.
In 2008, SIPO granted 411,982 patents, up 17.1 percent; 93,706 patents for invention were granted, an increase of 37.9 percent; among which, 352,406 were granted to domestic filers, representing 85.5 percent of the total and up 16.8 percent; 59,576 were granted to overseas filers, representing 14.5 percent of the total and up 18.8 percent. Invention patents granted to domestic filers accounted for 49.7 percent, further narrowing the gap with overseas filers.
As of Dec 31, 2008, SIPO had granted cumulative 2.5 million patents, 2.14 million of which were to domestic filers and 358,483 to overseas filers, representing 85.7 percent and 14.3 percent of the total respectively.
In 2008, 4,360 requests for reexamination were received, up 1,795 or 70 percent; 2,038 requests for invalidation were received, down 145 or 6.6 percent. Since 1985, the Patent Reexamination Board has received a total of 21,087 requests for invalidation.
In 2008, SIPO received 743 applications for registration of layout designs of integrated circuits, and 738 registrations were published and certificates issued. Since the implementation of the Regulation on Protection of Layout Designs of Integrated Circuits on October 1, 2001, SIPO had received a total of 2,551 applications for registration, and 1,564 registrations were published and certificates issued.
In 2008, Chinese nationals filed 6,089 PCT (patent cooperation treaty) applications, up 11.9 percent and ranking No 6 in the world. There were a total of 146 countries and regions filing patent applications in China.
In 2008, SAIC adopted a series of measures to accelerate trademark examination, with its workload in terms of trademark examination and opposition hitting record highs.
In 2008, the Trademark Office (TMO) of the SAIC received 698,000 trademark registration applications wherein the number of domestic trademark registration applications was 590,000, down 2.48 percent and the number of overseas trademark registration applications continued to rise rapidly reaching 108,000, up 4.85 percent. In 2008, TMO received 48,000 applications for the extension of registration, 25,000 applications for opposition, 89,000 for the change of registration entries, 68,000 for assignment and 18,000 for the deposit of licensing agreement.
Ensuring examination quality, TMO examined 750,000 trademark registration applications, up 85.2 percent. This was the first time the annual number of trademark registration applications examined exceeded the number of applications filed. In 2008, TMO approved a total of 403,000 registered trademarks over the year. The accumulative number of registered trademarks in China was 3.44 million. TMO handled 103,000 cases for change of registration entries, 72,000 for assignment, 60,000 for the extension of registration, 11,000 for opposition (up 26.75 percent), and 11,000 for the deposit of licensing agreements. TMO also dealt with 17,343 trademark registration applications filed by overseas companies via the International Bureau (one trademark covering multiple classes), up 4.9 percent and the accumulative number reached 131,801 (one trademark covering multiple classes), ranking No 1 in the world for the fourth consecutive year. Domestic companies filed 2,059 applications for international registration via TMO, up 12.7 percent as compared with that of 2007, the cumulative number reached 8,453 (one trademark covering multiple classes).
TMO accelerated the examination of geographical indications (GIs). From the beginning of 1994 to end of 2008, TMO registered in total 301 GIs, and 230 of which were registered in 2008, equivalent to 76 percent of the total in the first 15 years. By the end of 2008, TMO had granted 600,000 trademark registrations for agricultural products.
In 2008, the Trademark Review and Adjudication Board (TRAB) received 26,609 applications for review, up 51 percent compared with 2007. TRAB resolved 30,314 cases. Cases resolved exceeded cases filed for the first time. The number of pending cases dropped from 54,784 at the end of 2007 to 47,753, down 7031.
In 2008, NCAC promoted the registration of computer software. Software registration maintained steady and relevantly fast growth, registering 49,087 pieces of computer software, up 91.25 percent as compared with that of 2007. Monthly growth rates between September and December averaged over 100 percent compared with the same period in 2007. Software registrations totaled 47,398, up 93.3 percent and accounting for 96.56 percent of the total. Registrations of software copyright assignment or exclusive licensing agreement, registrations of software copyright pledging agreement and changes or addition of information to the existing registrations were 144, 109 and 1,436, up 200 percent, 9 percent and 43.6 percent respectively. Software registrations in 2008 equaled that of the combined total of 2006 and 2007.
In 2008, NCAC was committed to establishing and improving public participation in copyright protection and facilitating copyright management and trade.
The construction of collective management and collecting societies made great progress. China Audio-Video Copyright Association, China Written Works Copyright Society and China Photography Copyright Society were approved for establishment in May, November and December respectively and each held inaugural meetings. The swift development of the copyright trade promoted cultural innovation and development in China. Many works were exported overseas.
In 2008, the Ministry of Agriculture (MOA) and State Forestry Administration (SFA) strove to improve the protection of new varieties of plants.
By Dec 31, 2008, MOA had received cumulative 5,563 applications for new varieties of plants and granted 1,866. In 2008 alone, it received 868 and granted 449. Overseas users filed 273 applications and obtained 24 granted rights. In 2008, SFA received 77 applications, up 26 percent as compared with that of 2007. Up to end of 2008, it had granted cumulative 239 applications for new varieties of plants, representing 42 percent of the total.
(China Daily 06/08/2009 page9)
2013-07-17 Print
Print